Choosing the right business entity is a key decision for any business. The entity you pick can affect your tax bill, your personal liability and other issues. For many businesses, a limited liability company (LLC) is an attractive choice. It can be structured to resemble a corporation for owner liability purposes and a partnership for federal tax purposes. This duality may provide the owners with several benefits.

Like the shareholders of a corporation, the owners of an LLC (called members rather than shareholders or partners) generally aren’t liable for business debts except to the extent of their investment. Therefore, an owner can operate a business with the security of knowing that personal assets (such as a home or individual investment account) are protected from the entity’s creditors. This protection is far greater than that afforded by partnerships. In a partnership, the general partners are personally liable for the debts of the business. Even limited partners, if they actively participate in managing the business, can have personal liability.
Continue Reading
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become increasingly popular. According to Kelley Blue Book estimates, the EV share of the vehicle market in the U.S. was 7.6% in 2023, up from 5.9% in 2022. To incentivize the purchase of EVs, there’s a federal tax credit of up to $7,500 for eligible vehicles.

The tax break for EVs and fuel cell vehicles is called the Clean Vehicle Tax Credit. The current version of the credit was created under the Inflation Reduction Act. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions.
Continue Reading
When drafting partnership and LLC operating agreements, various tax issues must be addressed. This is also true of multi-member LLCs that are treated as partnerships for tax purposes. Here are some critical issues to include in your agreement so your business remains in compliance with federal tax law.

Identify and Describe Guaranteed Payments to Partners
For income tax purposes, a guaranteed payment is one made by a partnership that’s: 1) to the partner acting in the capacity of a partner, 2) in exchange for services performed for the partnership or for the use of capital by the partnership, and 3) not dependent on partnership income.
Continue Reading
Working from home has become increasingly common. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that about one out of five workers conducts business from home for pay. The numbers are even higher in certain occupational groups. About one in three people in management, professional and related occupations works from home.

Your Status Matters
If you work from a home office, you probably want to know: Can I get a tax deduction for the related expenses? It depends on whether you’re employed or in business for yourself.
Continue Reading
With Labor Day in the rearview mirror, it’s time to take proactive steps that may help lower your small business’s taxes for this year and next. The strategy of deferring income and accelerating deductions to minimize taxes can be effective for most businesses, as is the approach of bunching deductible expenses into this year or next to maximize their tax value.

Do you expect to be in a higher tax bracket next year? If so, then opposite strategies may produce better results. For example, you could pull income into 2024 to be taxed at lower rates, and defer deductible expenses until 2025, when they can be claimed to offset higher-taxed income.
Continue Reading
Believe it or not, there are ways to collect tax-free income and gains. Here are some of the best opportunities to put money in your pocket without current federal income tax implications:

- Roth IRAs offer tax-free income accumulation and withdrawals. Unlike withdrawals from traditional IRAs, qualified Roth IRA withdrawals are free from federal income tax. A qualified withdrawal is one that’s taken after you’ve reached age 59½ and had at least one Roth IRA open for over five years, or you are disabled or deceased. After your death, your heirs can take federal-income-tax-free qualified Roth IRA withdrawals, with proper planning.
Continue Reading
Partnerships are often used for business and investment activities. So are multi-member LLCs that are treated as partnerships for tax purposes. A major reason is that these entities offer federal income tax advantages, the most important of which is pass-through taxation. They also must follow some special and sometimes complicated federal income tax rules.

Governing Documents
A partnership is governed by a partnership agreement, which specifies the rights and obligations of the entity and its partners. Similarly, an LLC is governed by an operating agreement, which specifies the rights and obligations of the entity and its members. These governing documents should address certain tax-related issues. Here are some key points when creating partnership and LLC governing documents.
Continue Reading
Having a high income may mean you owe two extra taxes: the 3.8% net investment income tax (NIIT) and a 0.9% additional Medicare tax on wage and self-employment income. Let’s take a look at these taxes and what they could mean for you.

1. The NIIT
In addition to income tax, this tax applies on your net investment income. The NIIT only affects taxpayers with adjusted gross incomes (AGIs) exceeding $250,000 for joint filers, $200,000 for single taxpayers and heads of household, and $125,000 for married individuals filing separately.
Continue Reading
Let’s say you own real estate that has been held for more than one year and is sold for a taxable gain. Perhaps this gain comes from indirect ownership of real estate via a pass-through entity such as an LLC, partnership or S corporation. You may expect to pay Uncle Sam the standard 15% or 20% federal income tax rate that usually applies to long-term capital gains from assets held for more than one year.

However, some real estate gains can be taxed at higher rates due to depreciation deductions. Here’s a rundown of the federal income tax issues that might be involved in real estate gains.
Continue Reading
Navigating the complexities of tax law can be difficult, especially when faced with an unexpected tax bill due to the errors of a spouse or ex-spouse. The reason for such a bill has to do with the concept of “joint and several” liability. When a married couple files a joint tax return, each spouse is liable for the full amount of tax on the couple’s combined income. Therefore, the IRS can come after either spouse to collect the entire tax — not just the part that’s attributed to one spouse or the other. This includes any tax deficiency that the IRS assesses after an audit, as well as any penalties and interest.

There May Be Relief
In some cases, spouses are eligible for “innocent spouse relief.” This generally involves an individual who was unaware of a tax understatement that was attributable to his or her spouse. To qualify, you must show that you didn’t know about the understatement and that there was nothing that should have made you suspicious. In addition, the circumstances must make it inequitable to hold you liable for the tax.
Continue Reading
Federal estimated tax payments are designed to ensure that certain individuals pay their fair share of taxes throughout the year. If you don’t have enough federal tax withheld from your paychecks and other payments, you may have to make estimated tax payments. This is the case if you receive interest, dividends, self-employment income, capital gains, a pension or other income that’s not covered by withholding.

Individuals must pay 25% of a “required annual payment” by April 15, June 15, September 15, and January 15 of the following year, to avoid an underpayment penalty. If one of those dates falls on a weekend or holiday, the payment is due on the next business day.
Continue Reading
Savings bonds are purchased by many Americans, often as a way to help fund college or show their patriotism. Series EE bonds, which replaced Series E bonds, were first issued in 1980. From 2001 to 2011, they were designated as “Patriot Bonds” as a way for Americans “to express support for our nation’s anti-terrorism efforts,” according to the U.S. Treasury Department.

Perhaps you purchased some Series EE bonds many years ago and put them in a file cabinet or safe deposit box. Or maybe you bought them electronically and don’t think about them often. You may wonder: How is the interest you earn on EE bonds taxed? And if they reach final maturity, what steps do you need to take to ensure there’s no loss of interest or unanticipated tax consequences?
Continue Reading
Most businesses have websites today. Despite their widespread use, the IRS hasn’t issued formal guidance on when website costs can be deducted.

But there are established rules that generally apply to the deductibility of business expenses and provide business taxpayers launching a website with some guidance about proper treatment. In addition, businesses can turn to IRS guidance on software costs. Here are some answers to questions you may have.
Continue Reading
Many Americans receive disability income. Are you one of them, or will you soon be? If so, you may ask: Is the income taxed and if it is, how? It depends on the type of disability benefit and your overall income.

The key issue is: Who paid for the benefit? If the income is paid directly to you by your employer, it’s taxable to you just as your ordinary salary would be. (Taxable benefits are also subject to federal income tax withholding. However, depending on the employer’s disability plan, in some cases they aren’t subject to Social Security tax.)
Continue Reading
Divorce entails difficult personal issues, and taxes are probably the farthest thing from your mind. However, several tax concerns may need to be addressed to ensure that taxes are kept to a minimum and that important tax-related decisions are properly made. Here are six issues to be aware of if you’re in the process of getting a divorce.

1. Personal Residence Sale
In general, if a couple sells their home in connection with a divorce or legal separation, they should be able to avoid tax on up to $500,000 of gain (as long as they’ve owned and used the home as their principal residence for two of the previous five years). If one former spouse continues to live in the home and the other moves out (but they both remain owners of the home), they may still be able to avoid gain on the future sale of the home (up to $250,000 each), but special language may have to be included in the divorce decree or separation agreement to protect this tax exclusion for the spouse who moves out.
Continue Reading
While many facets of the economy have improved this year, the rising cost of living and other economic factors have caused many businesses to close their doors. If this is your situation, we can help you, including taking care of various tax responsibilities.

To start with, a business must file a final federal income tax return and some other related forms for the year it closes its doors.
Continue Reading
Are you buying a business that will have one or more co-owners? Or do you already own one fitting that description? If so, consider installing a buy-sell agreement.

A well-drafted agreement can do these valuable things:
- Transform your business ownership interest into a more liquid asset,
- Prevent unwanted ownership changes, and
- Avoid hassles with the IRS.
Continue Reading
If you own a closely held corporation, you can borrow funds from your business at rates that are lower than those charged by a bank. But it’s important to avoid certain risks and charge an adequate interest rate.

Basics of This Strategy
Interest rates have increased over the last couple years. As a result, shareholders may decide to take loans from their corporations rather than pay higher interest rates on bank loans. In general, the IRS expects closely held corporations to charge interest on related-party loans, including loans to shareholders, at rates that at least equal applicable federal rates (AFRs). Otherwise, adverse tax results can be triggered. Fortunately, the AFRs are lower than the rates charged by commercial lenders.
Continue Reading
If you’re a philanthropic individual who is also obligated to take required minimum distributions (RMDs) from a traditional IRA, you may want to consider a tax-saving strategy. It involves making a qualified charitable distribution (QCD).

How It Works
To reap the possible tax advantages of a QCD, you make a cash donation to an IRS-approved charity out of your IRA. This method of transferring IRA assets to charity leverages the QCD provision that allows IRA owners who are age 70½ or older to direct up to $105,000 of their IRA distributions to charity in 2024. (For married couples, each spouse can make QCDs for a possible total of $210,000.) When making QCDs, the money given to charity counts toward your RMDs but doesn’t increase your adjusted gross income (AGI) or generate a tax bill.
Continue Reading
If you’re selling property used in your trade or business, you should understand the tax implications. There are many complex rules that can potentially apply. To simplify this discussion, let’s assume that the property you want to sell is land or depreciable property used in your business, and has been held by you for more than a year.

Note: There are different rules for property held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business, intellectual property, low-income housing, property that involves farming or livestock, and other types of property.
Continue Reading
The current estate tax exemption amount ($13.61 million in 2024) has led many people to feel they no longer need to be concerned about federal estate tax. Before 2011, a much smaller exemption resulted in many people with more modest estates attempting to avoid it. But since many estates won’t currently be subject to estate tax, it’s a good time to devote more planning to income tax saving for your heirs.

Important: Keep in mind that the federal estate tax exclusion amount is scheduled to sunset at the end of 2025. Beginning on January 1, 2026, the amount is due to be reduced to $5 million, adjusted for inflation. Of course, Congress could act to extend the higher amount or institute a new amount.
Continue Reading
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the third quarter of 2024. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements.
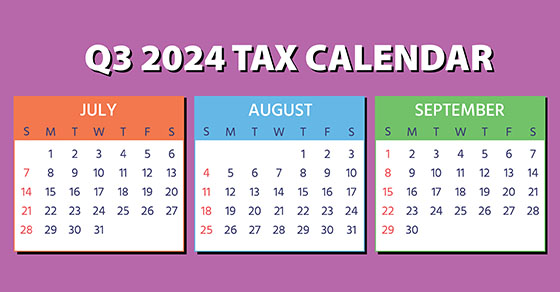
July 15
- Employers should deposit Social Security, Medicare, and withheld income taxes for June if the monthly deposit rule applies. They should also deposit nonpayroll withheld income tax for June if the monthly deposit rule applies.
Continue Reading
With school out, you might be hiring your child to work at your company. In addition to giving your son or daughter some business knowledge, you and your child could reap some tax advantages.

Benefits for Your Child
There are special tax breaks for hiring your offspring if you operate your business as one of the following:
- A sole proprietorship,
- A partnership owned by both spouses,
- A single-member LLC that’s treated as a sole proprietorship for tax purposes, or
- An LLC that’s treated as a partnership owned by both spouses.
Continue Reading
Employees, self-employed individuals and employers all pay Social Security tax, and the amounts can get bigger every year. And yet, many people don’t fully understand the Social Security tax they pay.

If You’re an Employee
If you’re an employee, your wages are hit with the 12.4% Social Security tax up to the annual wage ceiling. Half of the Social Security tax bill (6.2%) is withheld from your paychecks. The other half (also 6.2%) is paid by your employer, so you never actually see it. Unless you understand how the Social Security tax works and closely examine your pay statements, you may be blissfully unaware of the size of the tax. It’s potentially a lot!
Continue Reading
The IRS recently released guidance providing the 2025 inflation-adjusted amounts for Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). These amounts are adjusted each year, based on inflation, and the adjustments are announced earlier in the year than other inflation-adjusted amounts, which allows employers to get ready for the next year.

Fundamentals of HSAs
An HSA is a trust created or organized exclusively for the purpose of paying the qualified medical expenses of an account beneficiary. An HSA can only be established for the benefit of an eligible individual who is covered under a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). In addition, a participant can’t be enrolled in Medicare or have other health coverage (exceptions include dental, vision, long-term care, accident and specific disease insurance).
Continue Reading
Let’s say you own one or more vacant lots. The property has appreciated greatly and you’re ready to sell. Or maybe you have a parcel of appreciated land that you want to subdivide into lots, develop them and sell them off for a big profit. Either way, you’ll incur a tax bill.

For purposes of these examples, let’s assume that you own the vacant land directly as an individual or indirectly through a single-member LLC (SMLLC), a partnership or a multimember LLC that’s treated as a partnership for federal income tax purposes.
Continue Reading
After experiencing a downturn in 2023, merger and acquisition activity in several sectors is rebounding in 2024. If you’re buying a business, you want the best results possible after taxes. You can potentially structure the purchase in two ways:
- Buy the assets of the business, or
- Buy the seller’s entity ownership interest if the target business is operated as a corporation, partnership or LLC.

In this article, we’re going to focus on buying assets.
Continue Reading
If you donate valuable items to charity and you want to deduct them on your tax return, you may be required to get an appraisal. The IRS requires donors and charitable organizations to supply certain information to prove their right to deduct charitable contributions.

How Can You Protect Your Deduction?
First, be aware that in order to deduct charitable donations, you must itemize deductions. Due to today’s relatively high standard deduction amounts, fewer taxpayers are itemizing deductions on their federal returns than before the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act became effective in 2018.
Continue Reading
Many people dream of turning a hobby into a regular business. Perhaps you enjoy boating and would like to open a charter fishing business. Or maybe you’d like to turn your sewing or photography skills into an income-producing business.

You probably won’t have any tax headaches if your new business is profitable over a certain period of time. But what if the new enterprise consistently generates losses (your deductions exceed income) and you claim them on your tax return? You can generally deduct losses for expenses incurred in a bona fide business. However, the IRS may step in and say the venture is a hobby — an activity not engaged in for profit — rather than a business. Then you’ll be unable to deduct losses.
Continue Reading
There are several financial and legal implications when adding a new partner to a partnership. Here’s an example to illustrate: You and your partners are planning to admit a new partner. The new partner will acquire a one-third interest in the partnership by making a cash contribution to the business. Assume that your basis in your partnership interests is sufficient so that the decrease in your portions of the partnership’s liabilities because of the new partner’s entry won’t reduce your basis to zero.

More Complex Than It Seems
Although adding a new partner may appear to be simple, it’s important to plan the new person’s entry properly to avoid various tax problems.
Continue Reading































